
The company can, then, sell a new bond issuance at the new, lower interest rate. These are simplified examples, and the amounts of bond premiums and discounts in these examples are insignificant. In reality, bonds may be outstanding for a number of years, and related premiums and discounts can be substantial when millions of dollars of bonds are issued. These premiums and discounts are amortized using the effective interest method over the same number of periods as the related bonds are outstanding.
Recording the Issuance of Bonds at a Premium

They can also make transactions between businesses more efficient. A wine supplier typically doesn’t demand payment when it sells a case of wine to a restaurant and delivers the goods. It invoices the restaurant for the purchase to streamline the drop-off and make paying easier for the restaurant. Another way to calculate the interest expense when a bond is issued at a premium or discount is the effective interest rate method. The employer is also required by law to pay CPP (or QPP in Quebec) of an amount that equals the employee amount.
- Investors and creditors often use liquidity ratios to analyze how leveraged a company is.
- The descriptive information disclosed to readers of financial statements includes the interest rate and maturity date of the bond issue.
- However, too much Non-Current Liabilities will have the opposite effect.
- These debts are listed separately on the balance sheet to provide a more accurate view of a company’s current liquidity and ability to pay current liabilities as they become due.
Relationship with Other Financial Statements
It can also involve investing in other companies’ shares to enhance a special relationship or receive share dividends and capital appreciation of the shares as a return on investment. No matter the reason, there are important aspects of leveraging that must which of the following are long-term liabilities? be considered before entering into such an arrangement. AT&T clearly defines its bank debt that’s maturing in less than one year under current liabilities.
Recording the Issuance of Bonds at Face Value (at Par)

While these obligations enable companies to accomplish their near-term objective, they do create long-term concerns. Companies eventually need to settle all Bookkeeping for Chiropractors liabilities with real payments. If the obligations accumulate into an overly large amount, companies risk potentially being unable to pay the obligations. This is especially the case if the future obligations are due within a short time span of one another. This could create a liquidity crisis where there’s not enough cash to pay all maturing obligations simultaneously. Companies segregate their liabilities by their time horizon for when they’re due.
Debt ratios (such as solvency ratios) compare liabilities to assets. The ratios may be modified to compare the total assets to long-term liabilities only. Long-term liabilities refer to a company’s net sales non current financial obligations. On a balance sheet, a current portion of any long-term debt is listed in the current liabilities section. This provides a better picture of a company’s current liquidity.
The portion of a long-term liability, such as a mortgage, that is due within one year is classified on the balance sheet as a current portion of long-term debt. Additionally, a liability that is coming due may be reported as a long-term liability if it has a corresponding long-term investment intended to be used as payment for the debt. However, the long-term investment must have sufficient funds to cover the debt. You repay long-term liabilities over several years, such as 15 years. Sandra Habiger is a Chartered Professional Accountant with a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration from the University of Washington.

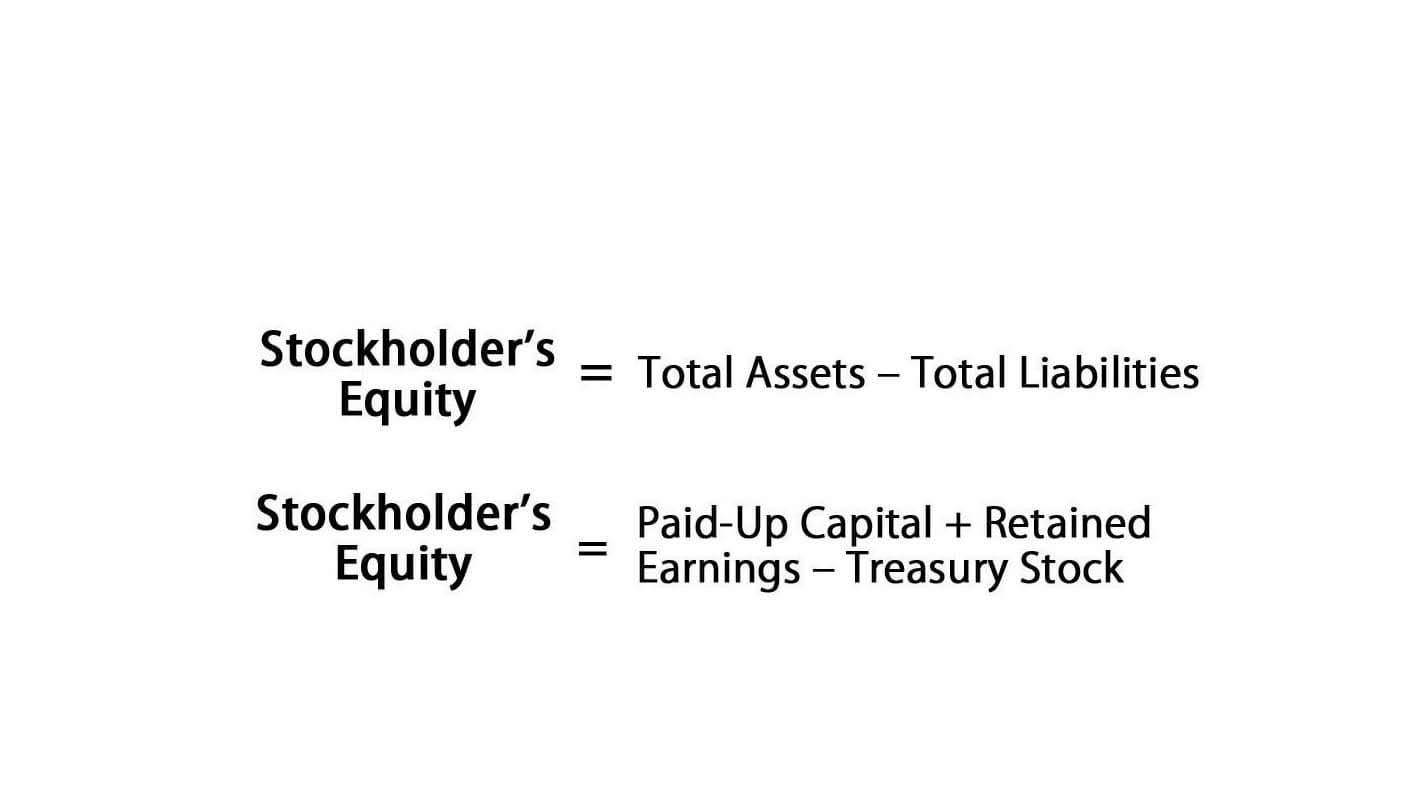
Stockholders’ Equity
Liabilities are categorized as current or non-current depending on their temporality. For example, on September 1, 2023, an investor purchases at face value, $100,000, 10-year, 8% bonds with interest payable each May 1 and November 1. On the maturity date of December 31, 2023, the interest expense of $80 is paid, bondholders are repaid, and the premium is written off as a reduction of interest expense. Each corporation issuing bonds has unique financing needs and attempts to satisfy various borrowing situations and investor preferences. Many types of bonds have been created to meet these varying needs. These rights are printed on the actual certificate and vary among bond issues.
Examples of Long-term Liabilities
- Also, a loan is repaid in equal blended payments over a period time.
- Keep in mind that long-term liabilities aren’t included with tax liabilities in order to provide more accurate information about a company’s debt ratios.
- To learn more about the components of stockholders’ equity, visit our topic Stockholders’ Equity.
- Investors are able to choose bonds with a term that agrees with their investment plans.
- AP typically carries the largest balances because they encompass day-to-day operations.
- The more stable a company’s cash flows, the more debt it can support without increasing its default risk.
This is called the face value of the bond; it is also referred to as the par-value of the bond. When the cash received is the same as a bond’s face value, the bond is said to be issued at par. A common face value of bonds is $1,000, although bonds of other denominations exist. A $30 million bond issue can be divided into 30,000 bonds, for example. This permits a large number of individuals and institutions to participate in corporate financing.
